
Occipital bone Encyclopedia Anatomy.app Learn anatomy 3D models, articles, and quizzes
Introduction: In controversial fashion, the presence of an enlarged external occipital protuberance has been recently linked to excessive use of handheld electronic devices.We sought to determine the prevalence of this protuberance in a diverse age group of adults from two separate time periods, before and approximately 10 years after the release of the iPhone, to further characterize this.

Study Young People are Developing ‘Hornlike Spikes’ at Back of Their Skull Due to Poor Posture
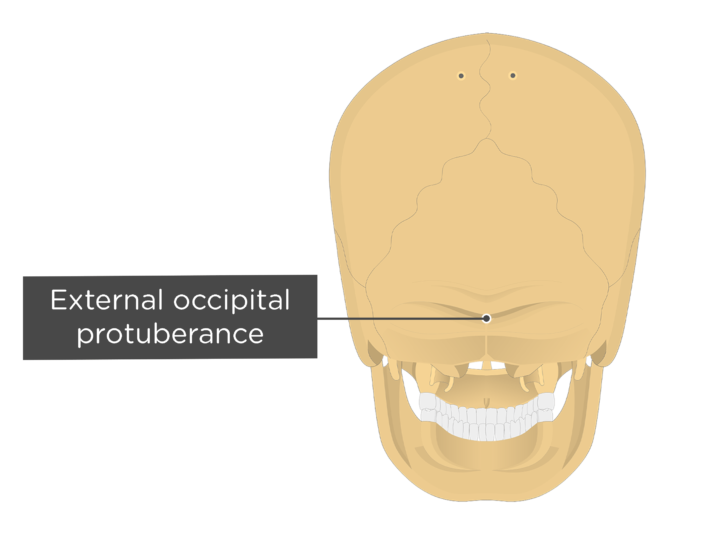
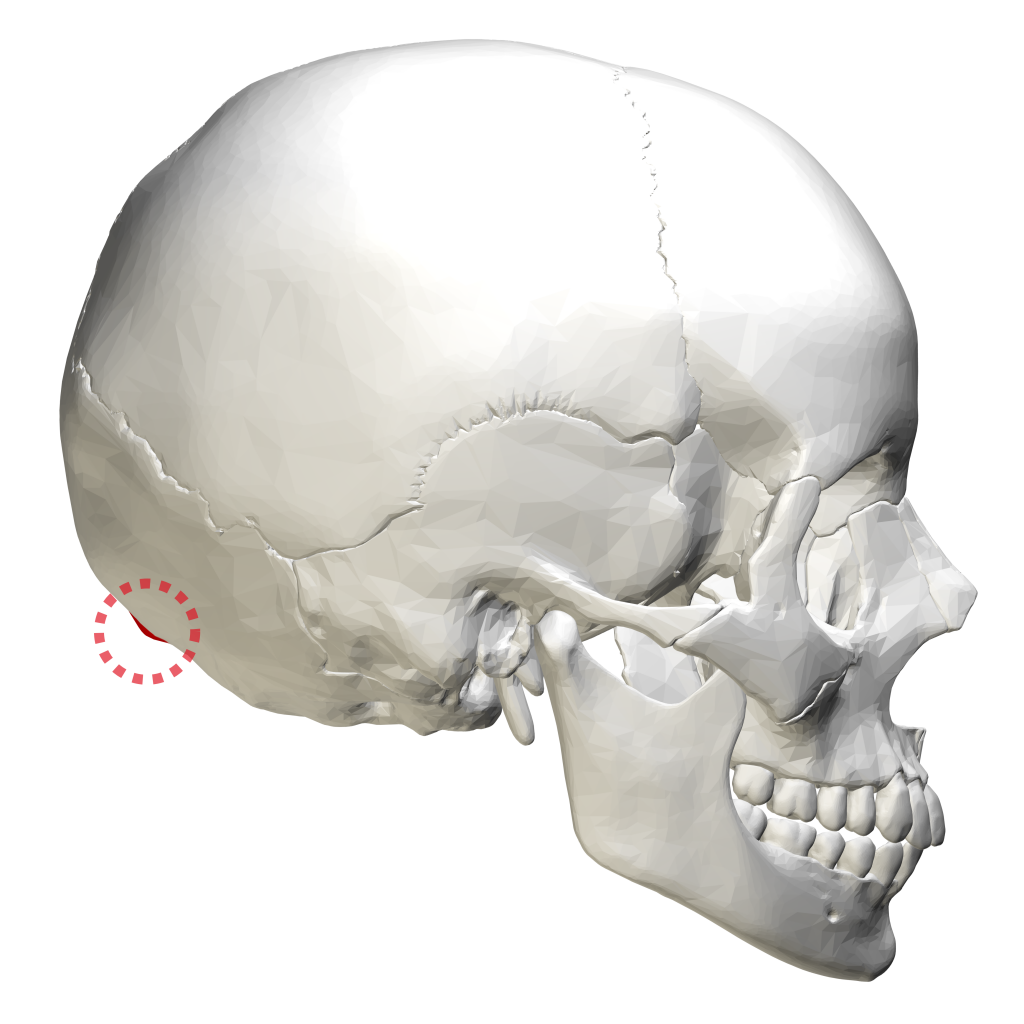
Near the middle of the squamous part of occipital bone is the external occipital protuberance, the highest point of which is referred to as the inion. The inion is the most prominent projection of the protuberance which is located at the posterioinferior (rear lower) part of the human skull. The nuchal ligament and trapezius muscle attach to it.
External Occipital Protuberance Massive External Occipital Protuberance Radiology Case
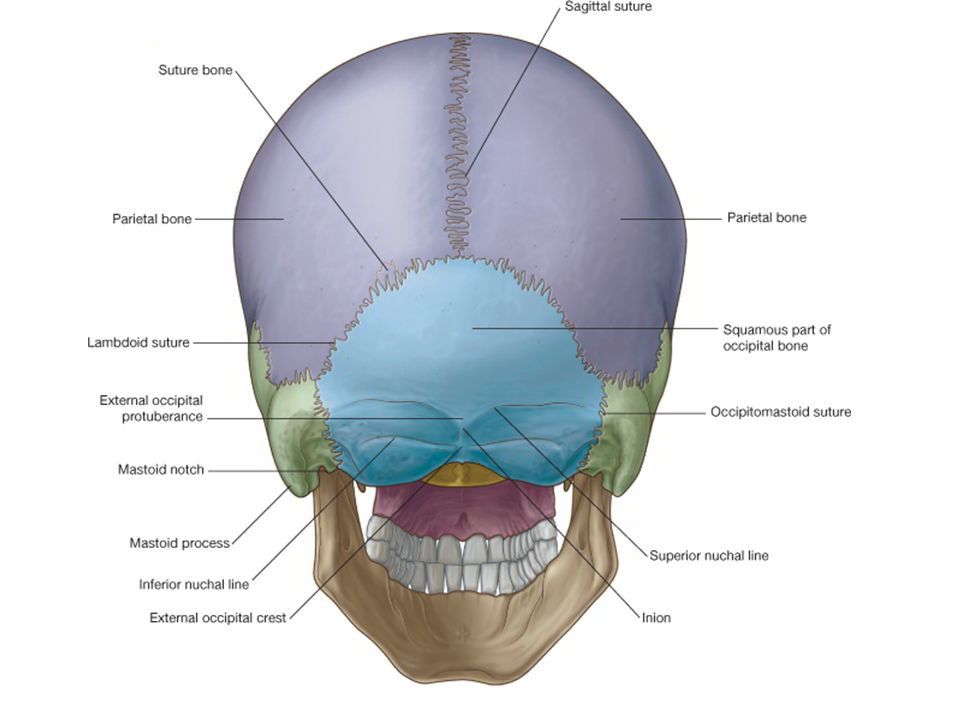
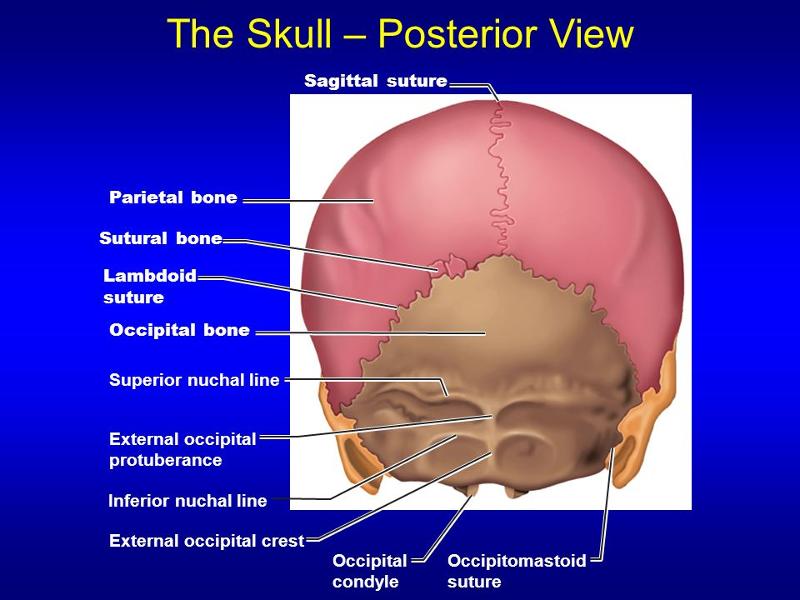
Extends from the midline of the occipital bone towards the lambdoid sutures on either side. Site of attachment of the epicranial aponeurosis. Superior nuchal line: Follows a similar trajectory to the supreme nuchal line but extends further. Marked in the midline by a palpable prominence - known as the external occipital protuberance.

External occipital protuberance (Protuberantia occipitalis externa); Image Yousun Koh Anatomi
Occipital Bone. The occipital bone is the single bone that forms the posterior skull and posterior cranial fossa (Figure 7.3.8; see also Figure 7.3.7). On its outside surface, at the posterior midline, is a small protrusion called the external occipital protuberance, which serves
External Occipital Protuberance Earth's Lab
Anatomy. A midline bump on back of head, on the external surface of satellite-dish-like vertical part (squama) of occipital bone, halfway between the foramen and its highest point. The highest nuchal lines run laterally from the protuberance, with the superior nuchal lines located slightly below.
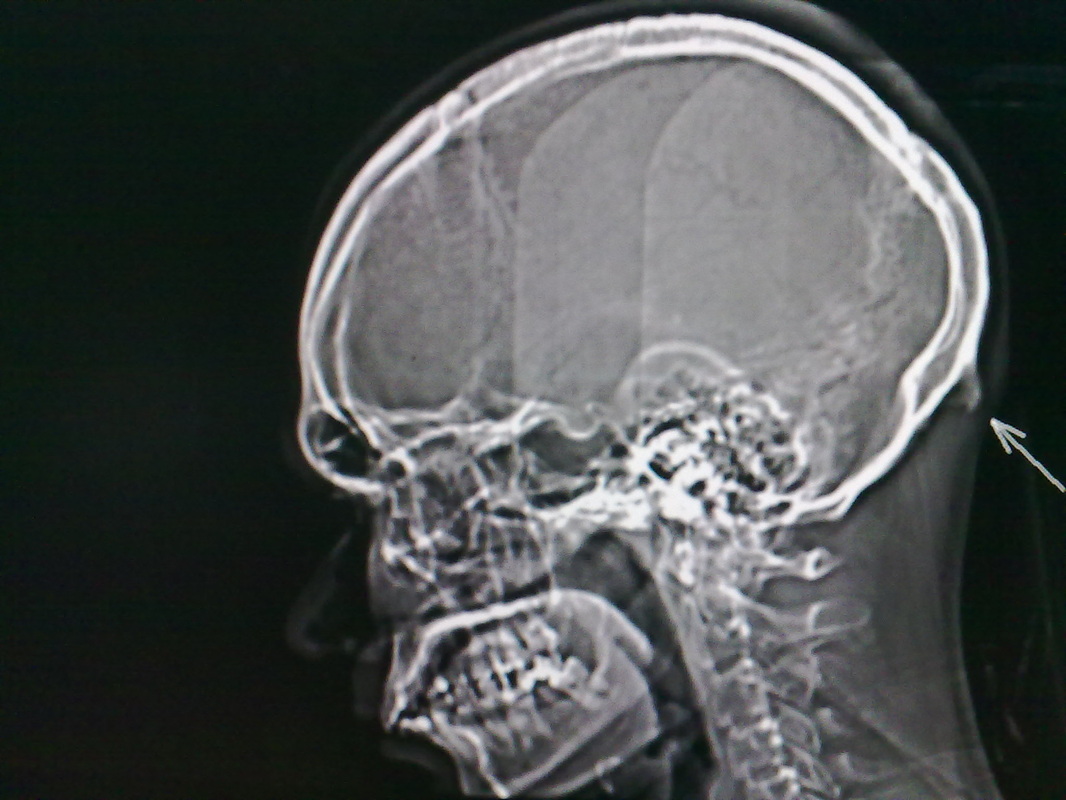
Prominent External Occipital Protuberance Radiology
The external occipital protuberance is a raised bump from the posterior most part of the occipital bone. Extending laterally from it on either side are the superior nuchal lines. The inion is the highest part of that protuberance. Sutures of the skull The lambdoid.
Norma occipitalis Earth's Lab
The bony skull bump — known as an external occipital protuberance — is sometimes so large, you can feel it by pressing your fingers on the base of your skull.

External Occipital Protuberance Photo by Bio223Lab_2009 Photobucket
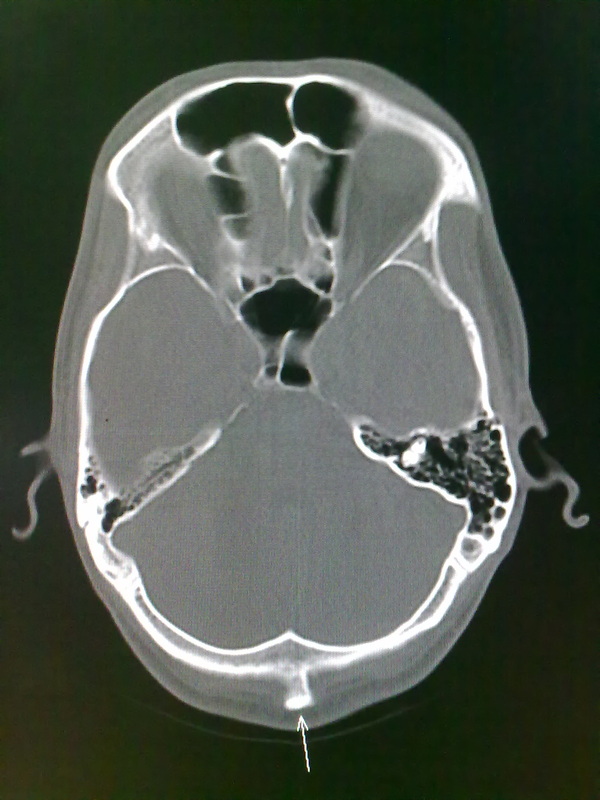
Case Discussion. External occipital protuberance is a midline bony prominence in the occipital bone that ligamentum nuchae and trapezius muscle attach to its tip. The tentorium cerebelli attaches to its internal surface. Exaggerated external occipital protuberance also is known as an occipital spur.

Protuberance Anatomy
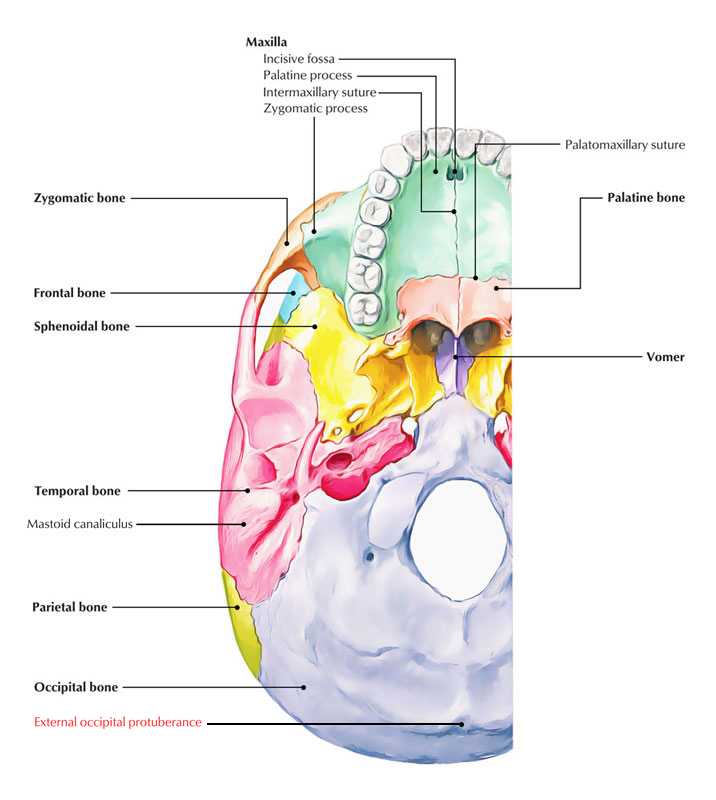
There is a small ridge of bone which arises from the squamous part of the occipital bone known as the external occipital crest. It acts as a site of attachment for the nuchal ligament. The parietal bones are difficult to visualise from the inferior view of the skull, however they can be seen articulating with the temporal and occipital bones.

Physical alignment do you have it? Take a minute & check. — LessWrong
Superiorly, the C1 vertebra articulates (forms a joint) with the occipital condyles of the skull. Inferiorly, C1 articulates with the C2 vertebra, and so on. Below these are the 12 thoracic vertebrae, designated T1-T12. The lower back contains the L1-L5 lumbar vertebrae.. out to the external occipital protuberance. It supports the skull.

External Occipital Protuberance Palpation / External occipital protuberance a site for
The occipital squama is the larger, more posterior portion of the external occipital bone. It is a thin, flat bone that forms the base of the skull and contributes to the formation of the posterior cranial fossa.The occipital squama is marked by several prominent features, including the external occipital protuberance, the external occipital crest, and the superior nuchal lines.

External occipital protuberance projecting as downward curved horn presenting with intractable
External occipital protuberance Protuberantia occipitalis externa. Definition. The under surface of the jugular process is rough, and gives attachment to the Rectus capitis lateralis muscle and the lateral atlantoöccipital ligament; from this surface an eminence, the paramastoid process,sometimes projects downward, and may be of sufficient.
The Physical Effects of Technology Saratoga Spine
At its midline is a prominence called the external occipital protuberance, with its highest point termed the inion. The superior nuchal line makes an intersection with a vertical midline ridge of bone called the medial nuchal line, which is also known as the external occipital crest, forming an uppercase "T" on the surface of the occipital.
Prominent External Occipital Protuberance Radiology
Occipital spurs, also called as occipital knob, occipital bun, chignon or inion hook, is an exaggerated external occipital protuberance (EOP). It is frequently discussed in anthropological literature as a Neanderthal trait but hardly reported and considered as a normal variant in medical literature. It is a frequent finding among males and hence a prominent occipital spur is often used in.
External Occipital Protuberance Inion My XXX Hot Girl
The external occipital protuberance is the palpable prominence found along the external aspect of the squamous part of occipital bone. It is located at the point along the midline where the occipital and nuchal planes meet. It consists of the inion, which is a craniometric point located at the tip of the external occipital protuberance. The.
What Is the External Occipital Protuberance? (with pictures)
External Occipital Protuberance (EOP) is an anatomical structure located on the occipital bone's posterior surface, at the superior nuchal line level. It is the insertion site of the nuchal ligament and the trapezius muscle [6, 16].